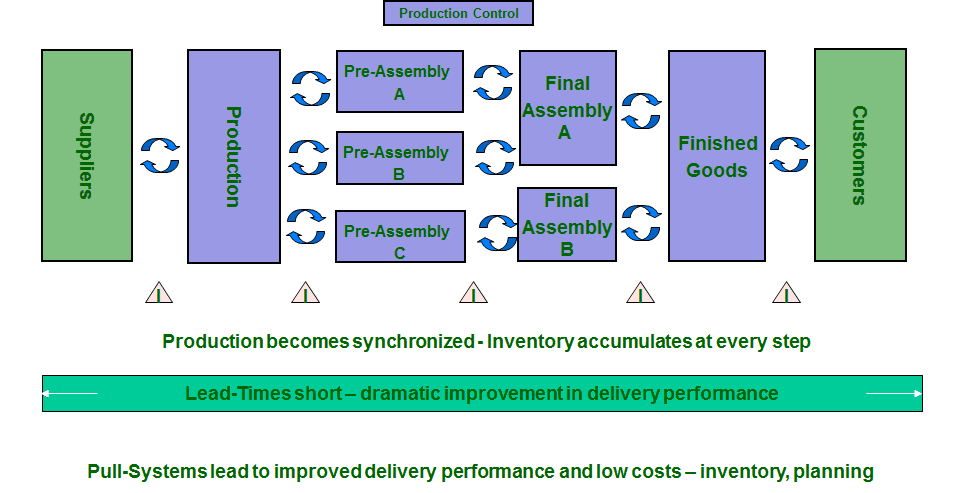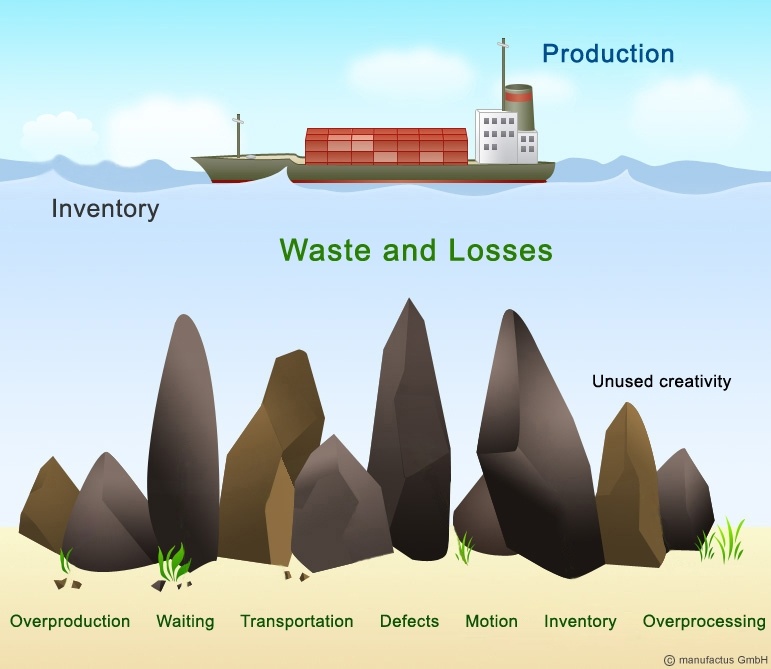
In order to become a world-class company it is fundamentally important to eliminate and to avoid all 7 types of waste (muda) in manufacturing and also in service processes.
How can we describe “waste”?
Any activity or process that adds costs but adds no value (for the customer).
There are 7 types of waste identified:
1) Overproduction
Overproduction arises when the company is producing more than the customer really requires. This may include both the production of products or components for which there are no orders, as well as production of more items than currently needed. This is the worst kind of waste, because it usually multiplies other kinds of waste. It increases rework rate, inventory, processing, waiting, as well as unnecessary motion and transportation.
 2) Inventory
2) Inventory
Inventory is the quantity of items on stock, which are required to manufacture a product. These goods also cause costs to the company. When they are not used they utilise valuable warehouse space, may become obsolete and may require raw materials, which cannot be used for more important goods. Competitive organisations make sure that their system controls the inventory, so that money is not being wasted on unwanted items or build groups.
3) Defects (scrap, rework)
Rework is required when products and components are defective or damaged and they have to be reworked. Defects are caused by bad manufacturing processes (caused by human or machine errors). Rework takes additional time and therefore increases manufacturing costs of the final product. In worst case scenario the items have to be discarded.
 4) Waiting times
4) Waiting times
Each step in a manufacturing process is dependent on the upstream and downstream stage processes. If employees, equipment, information or materials of the production process are delayed, production time is wasted and the cost of production will be increased.
5) (Unnecessary) Transportation
This includes the unnecessary movement of information, products or components from one area to another. Unnecessary transport usually occur together with unnecessary movement, product damages, lost parts and systems, which detect movements.
 6) (Unnecessary) Motion
6) (Unnecessary) Motion
Unnecessary movements occur when employee is moving around his work space and as a result of this may waste time and effort. All kind of unnecessary motion is being caused by poor working standard practices, poor (not optimal) process design or work area layout.
7) Overprocessing
Overprocessing includes also extra steps in the manufacturing process which need to be taken. It can also mean producing products of a higher quality than required. This may be due to incorrectly used equipment, errors in rework process, poor process design or bad communication. This can be also result of not checking what are the real customers’ requirements.
 8) Not used creativity of employees
8) Not used creativity of employees
This waste involves lost of time, skills, ideas, improvements and learning opportunities by not taking employees opinion into the account. This is result of employees not taking part in design of manufacturing processes. Only in this way the ideas can develop, which are needed to eliminate and avoid the other seven waste sources. This helps to improve your processes in continuous manner by increasing the available knowledge and creativity of you employees. In addition it helps in principle to increase the level of employees satisfaction at work.
++ KANBAN ONLINE PORTALS ++
IKS – Integrated Kanban System
Best electronic Kanban – made by real Kanban Experts
Learn more about e-KANBAN System IKS on: www.e-kanban.com
SMART KANBAN
The cost efficient solution for Kanban introduction – optimized for pure manual Kanban
Learn more about SMART KANBAN on: www.kanban-system.com
LEAN / KANBAN
Click on the desired topic to learn more.