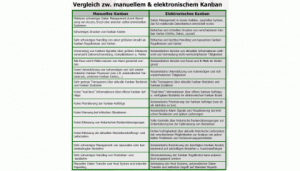
How to achieve a Kanban implementation / introduction with less difficulties or problems, which simple Kanban rules are helpful?
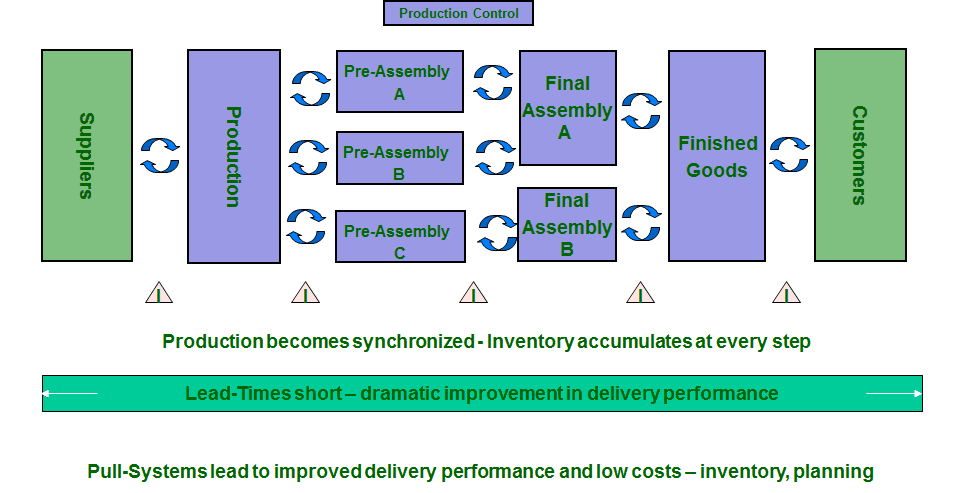
More and more companies recognize the benefits and huge potential of “real” Lean Kanban pull systems against classical ERP / MRP based processes which are normally created on push logic.
To manage the material flow by a pull system, most companies are using the Kanban principle. Kanban is easy to understand and it is based on so called “self controlling loops” which is reducing the administrative effort in daily business to a minimum.
Without basic Kanban rules, the implementation of a Kanban system sometimes creates difficulties or causes problems!
For this reason we have summarized some typical mistakes in the Kanban implementation / introduction process (of course, there exist some more topics which can also cause problems, but we think theses are some of the most important ones).
Additionally we have added some tips which you should think about to avoid the described mistakes and to implement a Kanban system successfully right on from the beginning.
Of course, all related activities to improve and optimize the existing production and logistic processes (KAIZEN) are absolutely required to create the perfect environment for a Kanban system!
Here is the list of typical mistakes and our tips how to avoid these mistakes:
Mistake 1: Selection of wrong Kanban parts
The items have not been analyzed (correctly) and the criteria for Kanban parts haven’t been defined.
So parts are managed by Kanban which make no sense or can only be handled with difficulties.
Our tips: Start with an ABC-XYZ analysis!
Especially an ABC analysis can normally be realized in a fast and easy way. Such an analysis is a great starting point to get a “better feeling” of your own parts.
Mistake 2: No Kanban Coordinator
There is no person defined which is responsible for the management and the optimization of the Kanban system. The Kanban coordinator is normally also the contact person no. 1 for all operators and people at the shop-floor.
Our tips: Define a Kanban Coordinator at the very beginning!
Organize training courses for this person, give him/her the right lean tools for the efficient lean Kanban data management to guarantee the required support in case of problems.
Especially during the Kanban implementation phase this is not a “part time job”!
Mistake 3: No stable lean basis to manage Kanban data
The Kanban data is managed in an (complex) Excel-Spreadsheet, ERP / MRP System or a similar tool. The management of the Kanban data gets more and more complex and is very time consuming.
Our tips: Start with a lean and stable Kanban friendly data basis, because using a special Kanban tool which is prepared especially for Kanban requirements and which is approved by a lot of other Kanban users will reduce the required time for Kanban data management, card printing and Kanban controlling to a minimum! Don`t waste your time struggling with lean basic principles or “so called” Kanban MRP / ERP Add-Ons!
Your employees will thank you for givimg them the right tools up from the beginning and not afterwards after loosing a lot of money and energy!
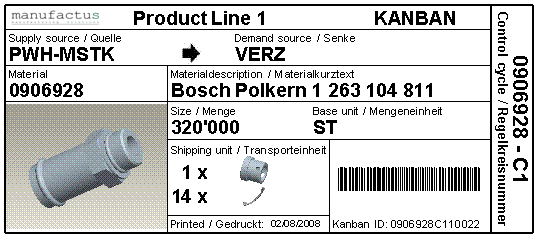
Mistake 4: No standardized Kanban cards
The Kanban cards are created and printed with Word, Excel or another similar tool. There is no clear standard defined and the Kanban data on the cards are not complete or not 100% correct.
Our tips: Define standard Kanban cards (maybe also different sizes of the Kanban cards for different container types).
Make sure that the Kanban cards can be created and printed in a fast and easy way.
Mistake 5: The production lot-sizes are too huge
The production lot-sizes of the Kanban parts are too big. This causes a huge amount of Kanban cards which cannot be handled in an easy way in operation.
Our tips: Work continuously on the reduction of your production lot-sizes and your set-up times. This is a very important topic for a successful Kanban system, for the flexibility of the production and for all other processes. Sometimes production lot-sizes can be “cut off” and the production is still running without any problems nethertheless.
Mistake 6: The Kanban processes are too complex
If the Kanban processes are too complex => human errors are guaranteed. This results in “lost” Kanban cards and a very bad transparency.
Our tips: Define easy and clear processes which can be handled by each employee. Define clear responsibilities and transparent processes (Kanban collection points, visualization of information, Kanban rules,…).
Mistake 7: No required KAIZEN activities
A Kanban system expose existing weaknesses very fast (bad quality, high production lot-sizes and set-up times etc. etc.) but no activities are defined and realized to solve this problems to prepare the required environment.
Our tips: Make a note of all problems and weaknesses!
Discuss all topics inside a team and define the required actions and projects!
Start with the required optimization activities fast!
Please do not forget: Kanban is a strong tool, but it is only one part of the big LEAN puzzle and Kanban does not solve all of your problems automatically!
Do you have more questions regarding the Lean Kanban implementation process?
Our final tip (the best): Please contact us, because we are able to help you saving a lot of time and money!
++ KANBAN ONLINE PORTALS ++
IKS – Integrated Kanban System
Best electronic Kanban – made by real Kanban Experts
Learn more about e-KANBAN System IKS on: www.e-kanban.com
SMART KANBAN
The cost efficient solution for Kanban introduction – optimized for pure manual Kanban
Learn more about SMART KANBAN on: www.kanban-system.com
LEAN / KANBAN
Click on the desired topic to learn more.